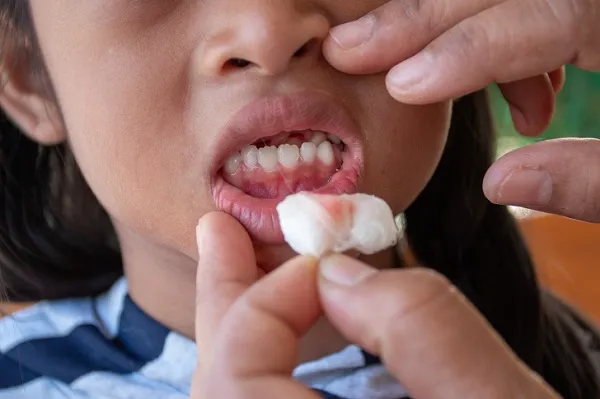
Bleeding gums in children is evidence of problems with the child’s teeth resulting either from pollution or from following an unhealthy diet and in this article, we will learn about this problem, what its symptoms are, and how it can be solved.
What is bleeding gums in children?
Bleeding gums in children is a sign of inflammation of the gums resulting from the accumulation of bacteria on the layer of plaque, causing this bleeding and also leading to dry mouth and in most cases, the main cause of this bleeding is eating large amounts of sugar, which is considered the preferred meal for bacteria.
What are the symptoms of bleeding gums in children?
- Bleeding gums in children are accompanied by several symptoms, the most prominent of which are:
- Receding gums
- Blistering in the mouth
- Swelling of the gums
- Significant redness on the gums
- Change in gum color
- Appearance of odor in the mouth
- Causes of bleeding gums in children
- There are many reasons that lead to bleeding gums in a child, such as:
- Vitamin K deficiency
- An unhealthy diet
- Eating too much sugar
- Neglecting to clean and care for teeth
- The presence of infections in the mouth and teeth that lead to bleeding
- Tooth decay
- Lime build-up
Treatment of bleeding gums in children
- Treatment of bleeding gums includes several steps:
- Visit the dentist: Parents should bring the child to the dentist to evaluate his condition and determine the main cause of bleeding gums.
- Teaching proper oral hygiene: The child must be taught how to brush his teeth properly using a brush, medical floss, and mouthwash appropriate for his age.
- Brushing teeth regularly: The child should brush his teeth regularly after every meal using a soft toothbrush.
- Reducing harmful foods: Sugary and crunchy foods should be avoided, which increase plaque accumulation and irritate the gums.
- Reducing tartar: The dentist may need to remove tartar from the teeth to improve gum health.
- Drug treatment: In some severe cases, the dentist may recommend applying anti-inflammatory ointments to the gums or prescribing antibiotics.
- Regular visits to the dentist: It is important for the child to make regular visits to the dentist for examination, evaluation, and prevention of future gum problems.
- By following these instructions, you will notice that the bleeding in the child’s gums stops within 7-10 days
Read also: